Response.RedirectPermanent in .NET 3.5 and older
One of the new features in ASP.NET 4.0 is permanently redirecting to a page using Response.RedirectPermanent.
It is common practice in Web applications to move pages and other content around over time, which can lead to an accumulation of stale links in search engines. In ASP.NET, developers have traditionally handled requests to old URLs by using by using the Response.Redirect method to forward a request to the new URL. However, the Redirect method issues an HTTP 302 Found (temporary redirect) response, which results in an extra HTTP round trip when users attempt to access the old URLs.
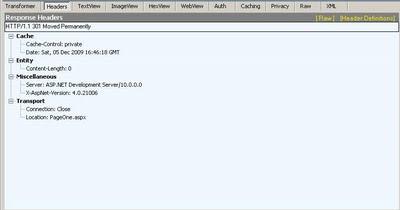
You can achieve this functionality in ASP.NET 3.5 and older by writing a
301 Moved Permanently Status and
a ``Location Header to theResponse` stream. This can be found in the HTTP
specifications.
Here is an example.
Response.Clear();
Response.Status = "301 Moved Permanently";
Response.AddHeader("Location", "PageOne.aspx");
Response.End();
You can verify the result by using Fiddler.