Handling the AggregateException
Last week I showed you how you can use the AggregateException to apply
consistent exception handling in batch operations. You can find that
post
here.
Bart De Smet read that post and pointed out that I should check out the Handle method of the AggregateException.
The Handle method
As found in the MSDN documentation.
Description
Invokes a handler on each Exception contained by this AggregateException.
Parameters
System.Func<Exception, Boolean> predicate
The predicate to execute for each exception. The predicate accepts as an argument the Exception to be processed and returns a Boolean to indicate whether the exception was handled.
Remarks
Each invocation of the predicate returns true or false to indicate whether the Exception was handled. After all invocations, if any exceptions went unhandled, all unhandled exceptions will be put into a new AggregateException which will be thrown. Otherwise, the Handle method simply returns. If any invocations of the predicate throws an exception, it will halt the processing of any more exceptions and immediately propagate the thrown exception as-is.
In practice
I refactored the example in my previous
post to make use of the Handle method.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
ExecuteBatch();
}
catch (AggregateException aggEx)
{
aggEx.Handle(HandleBatchExceptions);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
I’m passing a Func<T, TResult>
delegate to the
Handle method. In this delegate I decide whether I’m handling the
exception or not. If I handle the exception, I return true, else I
return false.
private static bool HandleBatchExceptions(Exception exceptionToHandle)
{
if (exceptionToHandle is ArgumentNullException)
{
// I'm handling the ArgumentNullException.
Console.WriteLine("Handling the ArgumentNullException.");
// I handled this Exception
return true;
}
else
{
// I'm only handling ArgumentNullExceptions.
Console.WriteLine(string.Formaxt("I'm not handling the {0}.", exceptionToHandle.GetType()));
//I didn't handle this Exception, return false.
return false;
}
}
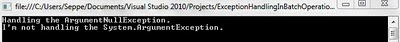
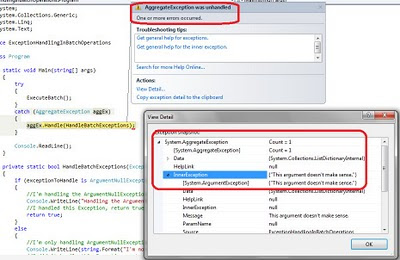
When we run this example a new AggregateException is thrown with the
exceptions I didn’t handle.
Conclusion
Make use of the Handle method to run over each InnerException and decide which exception you want to handle or not. The exceptions you didn’t handle are automatically wrapped in a new AggregateException which gets rethrown.